a = 71 #Identifies a as class<int>
b = 88.44 #Identifies b as class<float>
name = “Raushan” #Identifies name as class<Str>
Rules for defining a variable name: (Also applicable to other identifiers)
- A variable name can contain alphabets, digits, and underscore.
- A variable name can only start with an alphabet and underscore.
- A variable can’t start with a digit.
- No white space is allowed to be used inside a variable name.
Examples of few valid variable names,
Raushan, raushan, one8, _akki, aakash, raushan_bro, etc.
Operators in Python
The following are some common operators in Python:
- Arithmetic Operators (+, -, *, /, etc.)
- Assignment Operators (=, +=, -=, etc.)
- Comparison Operators (==, >=, <=, >, <, !=, etc.)
- Logical Operators (and, or, not)
type() function and Typecasting
type function is used to find the data type of a given variable in Python.
a = 31
type(a) #class<int>
b = “31”
type(b) #class<str>A number can be converted into a string and vice versa (if possible)
There are many functions to convert one data type into another.
Str(31) # ”31” Integer to string conversion
int(“32”) # 32 String to int conversion
float(32) #32.0 Integer to float conversion… and so on
Here “31” is a string literal, and 31 is a numeric literal.
input() function
This function allows the user to take input from the keyboard as a string.
a = input(“Enter name”) #if a is “Raushan”, the user entered RaushanNote: The output of the input function is always a string even if the number is entered by the user.
Suppose if a user enters 34, then this 34 will automatically convert to “34” string literal.
Chapter 2 – Practice Set
- Write a Python program to add two numbers.
- Write a Python program to find the remainder when a number is divided by Z(Integer).
- Check the type of the variable assigned using the input() function.
- Use a comparison operator to find out whether a given variable a is greater than b or not. (Take a=34 and b=80)
- Write a Python program to find the average of two numbers entered by the user.
- Write a Python program to calculate the square of a number entered by the user.
Chapter 3 – Strings
The string is a data type in Python.
A string is a sequence of characters enclosed in quotes.
We can primarily write a string in three ways:
- Single quoted strings : a = ‘Raushan’
- Double quoted strings : b = “Raushan”
- Triple quoted strings : c = ’’’ Raushan ’’’
String Slicing:
A string in Python can be sliced for getting a part of the string.
Consider the following string:
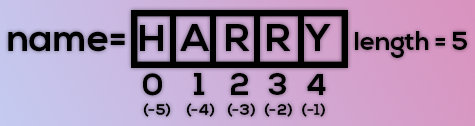
The index in a string starts from 0 to (length-1) in Python. To slice a string, we use the following syntax:

Negative Indices: Negative indices can also be used as shown in the figure above. -1 corresponds to the (length-1) index, -2 to (length-2).
Slicing with skip value
We can provide a skip value as a part of our slice like this:
word = “amazing”
word[1:6:2] # It will return ’mzn’Other advanced slicing techniques
word = ‘amazing’
word[:7] or word[0:7] #It will return ‘amazing’
word[0:] or word[0:7] #It will return ‘amazing’String Functions
Some of the most used functions to perform operations on or manipulate strings are:
- len() function : It returns the length of the string.
len(‘Raushan’) #Returns 7- endswith(“han”) : This function tells whether the variable string ends with the string “han” or not. If string is “Raushan”, it returns for “han” since Raushan ends with han.
- count(“a”) : It counts the total number of occurrences of any character.
- capitalize() : This function capitalizes the first character of a given string.
- find(word) : This function finds a word and returns the index of first occurrence of that word in the string.
- replace(oldword, newword) : This function replaces the old word with the new word in the entire string.
Escape Sequence Characters:
Sequence of characters after backslash ‘\’ [Escape Sequence Characters]
Escape Sequence Characters comprises of more than one character but represents one character when used within the string.
Examples: \n (new line), \t (tab), \’ (single quote), \\ (backslash), etc.
Chapter 3 – Practice Set
- Write a Python program to display a user-entered name followed by Good Afternoon using input() function.
- Write a program to fill in a letter template given below with name and date.
letter = ‘’’ Dear <|NAME|>,
You are selected!
<|DATE|>- Write a program to detect double spaces in a string.
- Replace the double spaces from problem 3 with single spaces.
- Write a program to format the following letter using escape sequence characters.
letter = “Dear Raushan, This Python course in nice. Thanks!!”Chapter 4 – Lists and Tuples
Python Lists are containers to store a set of values of any data type.
friends = [‘Apple’, ‘Akash’, ‘Rohan’, 7, False]The list can contain different types of elements such as int, float, string, Boolean, etc. Above list is a collection of different types of elements.
List Indexing
A list can be index just like a string.
L1 = [7, 9, ‘Raushan’]
L1[0] – 7
L1[1] – 9
L1[70] – Error
L1[0:2] – [7,9] (This is known as List Slicing)List Methods
Consider the following list:
L1 = [1, 8, 7, 2, 21, 15]- sort() – updates the list to [1,2,7,8,15,21]
- reverse() – updates the list to [15,21,2,7,8,1]
- append(8) – adds 8 at the end of the list
- insert(3,8) – This will add 8 at 3 index
- pop(2) – It will delete the element at index 2 and return its value
- remove(21) – It will remove 21 from the last
Tuples in Python:
A tuple is an immutable (can’t change or modified) data type in Python.
a = () #It is an example of empty tuple
a = (1,) #Tuple with only one element needs a comma
a = (1, 7, 2) #Tuple with more than one elementOnce defined, tuple elements can’t be manipulated or altered.
Tuple methods:
Consider the following tuple,
a = (1, 7, 2)- count(1) – It will return the number of times 1 occurs in a.
- index(1) – It will return the index of the first occurrence of 1 in a.
Chapter 4 – Practice Set
- Write a program to store seven fruits in a list entered by the user.
- Write a program to accept the marks of 6 students and display them in a sorted manner.
- Check that a tuple cannot be changed in Python.
- Write a program to sum a list with 4 numbers.
- Write a program to count the number of zeros in the following tuple:
a = (7, 0, 8, 0, 0, 9)Chapter 5 – Dictionary and Sets
Dictionary is a collection of key-value pairs.
Syntax:
''' a = {“key”: “value”,
“Raushan”: “code”,
“marks” : “100”,
“list”: [1,2,9]}
a[“key”] # Prints value
a[“list”] # Prints [1,2,9] '''
Properties of Python Dictionaries
- It is unordered
- It is mutable
- It is indexed
- It cannot contain duplicate keys
Dictionary Methods
Consider the following dictionary,
a = {“name”: “Raushan”,
“from”: “India”,
“marks”: [92,98,96]}- items() : returns a list of (key,value) tuple.
- keys() : returns a list containing dictionary’s keys.
- update({“friend”: “Sam”}) : updates the dictionary with supplied key-value pairs.
- get(“name”) : returns the value of the specified keys (and value is returned e.g., “Raushan” is returned here)
More methods are available on docs.python.org
Sets in Python
Set is a collection of non-repetitive elements.
S= Set() # No repetition allowed!
S.add(1)
S.add(2)
# or Set = {1,2}If you are a programming beginner without much knowledge of mathematical operations on sets, you can simply look at sets in python as data types containing unique values.
Properties of Sets
- Sets are unordered # Elements order doesn’t matter
- Sets are unindexed # Cannot access elements by index
- There is no way to change items in sets
- Sets cannot contain duplicate values
Operations on Sets
Consider the following set:
S = {1,8,2,3}- Len(s) : Returns 4, the length of the set
- remove(8) : Updates the set S and removes 8 from S
- pop() : Removes an arbitrary element from the set and returns the element removed.
- clear() : Empties the set S
- union({8, 11}) : Returns a new set with all items from both sets. #{1,8,2,3,11}
- intersection({8, 11}) : Returns a set which contains only items in both sets. #{8}
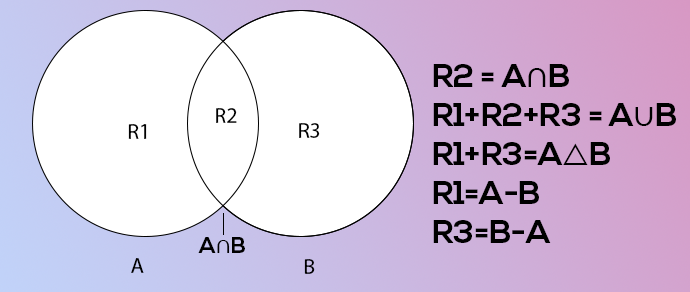
Chapter 5 – Practice Set
- Write a program to create a dictionary of Hindi words with values as their English translation. Provide the user with an option to look it up!
- Write a program to input eight numbers from the user and display all the unique numbers (once).
- Can we have a set with 18(int) and “18”(str) as a value in it?
- What will be the length of the following set S:
S = Set()
S.add(20)
S.add(20.0)
S.add(“20”)What will be the length of S after the above operations?
- S = {}, what is the type of S?
- Create an empty dictionary. Allow 4 friends to enter their favorite language as values and use keys as their names. Assume that the names are unique.
- If the names of 2 friends are the same; what will happen to the program in Program 6?
- If the languages of two friends are the same; what will happen to the program in Program 6?
- Can you change the values inside a list which is contained in set S
S = {8, 7, 12, “Raushan”, [1, 2]}Chapter 6 – Conditional Expressions
Sometimes we want to play pubg on our phone if the day is Sunday.
Sometimes we order Ice-cream online if the day is sunny.
Sometimes we go hiking if our parents allow.
All these are decisions that depend on the condition being met.
In python programming too, we must be able to execute instructions on a condition(s) being met. This is what conditions are for!
If else and elif in Python
If else and elif statements are a multiway decision taken by our program due to certain conditions in our code.
Syntax:
'''
if (condition1): // if condition 1 is true
print(“yes”)
elif (condition2): // if condition 2 is true
print(“No”)
else: // otherwise
print(“May be”)
'''
Code example:
a = 22
if (a>9):
print(“Greater”)
else:
print(“lesser”)Quick Quiz: Write a program to print yes when the age entered by the user is greater than or equal to 18.
Relational Operators
Relational operators are used to evaluate conditions inside if statements. Some examples of relational operators are:
= = -> equals
>= -> greater than/equal to
<=, etc.Logical Operators
In python, logical operators operate on conditional statements. Example:
and -> true if both operands are true else false
or -> true if at least one operand is true else false
not -> inverts true to false and false to trueelif clause
elif in python means [else if]. If statement can be chained together with a lot of these elif statements followed by an else statement.
'''
if (condition1):
#code
elif (condition 2):
#code
elif (condition 2):
#code
….
else:
#code '''
- The above ladder will stop once a condition in an if or elif is met.
Important Notes:
- There can be any number of elif statements.
- Last else is executed only if all the conditions inside elifs fail.
Chapter 6 – Practice Set
- Write a program to find the greatest of four numbers entered by the user.
- Write a program to find out whether a student is pass or fail if it requires a total of 40% and at least 33% in each subject to pass. Assume 3 subjects and take marks as an input from the user.
- A spam comment is defined as a text containing the following keywords:
“make a lot of money”, “buy now”, “subscribe this”, “click this”. Write a program to detect these spams.
- Write a program to find whether a given username contains less than 10 characters or not.
- Write a program that finds out whether a given name is present in a list or not.
- Write a program to calculate the grade of a student from his marks from the following scheme:
| 90-100 | Ex |
| 80-90 | A |
| 70-80 | B |
| 60-70 | C |
| 50-60 | D |
| <50 | F |
- Write a program to find out whether a given post is talking about “Raushan” or not.